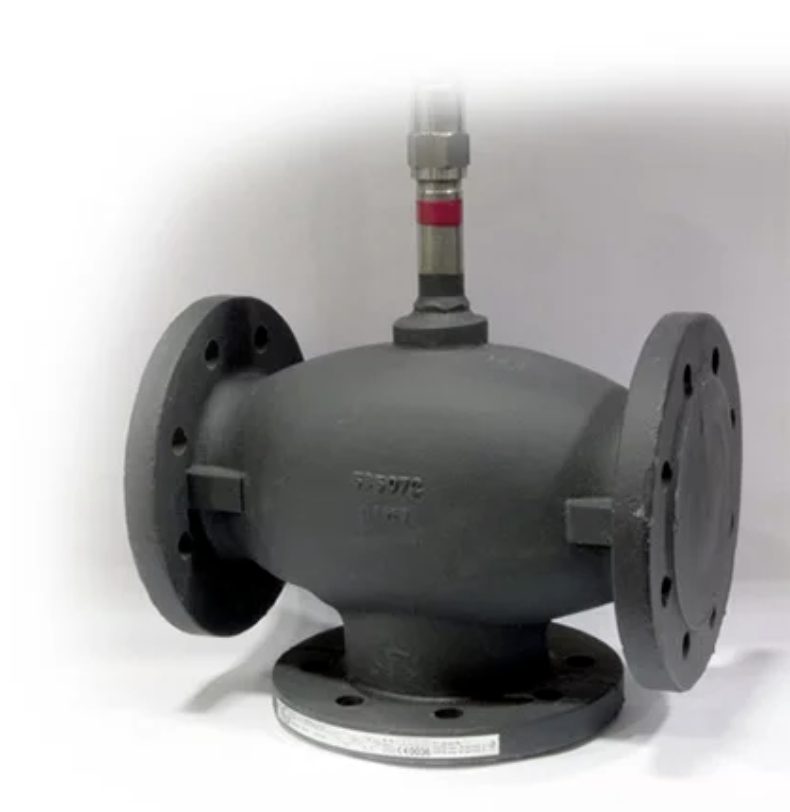
Mixing and diverting valves are used to provide reliable flow and pressure control in systems by mixing or diverting fluids or gasses. Also known as 3-way control valves, they are ideal for use with hot or cold water, oil, or steam applications. They are installed in many types of industrial equipment and machinery, including engines, compressors, steam desuperheaters, and lubrication oil cooling systems.
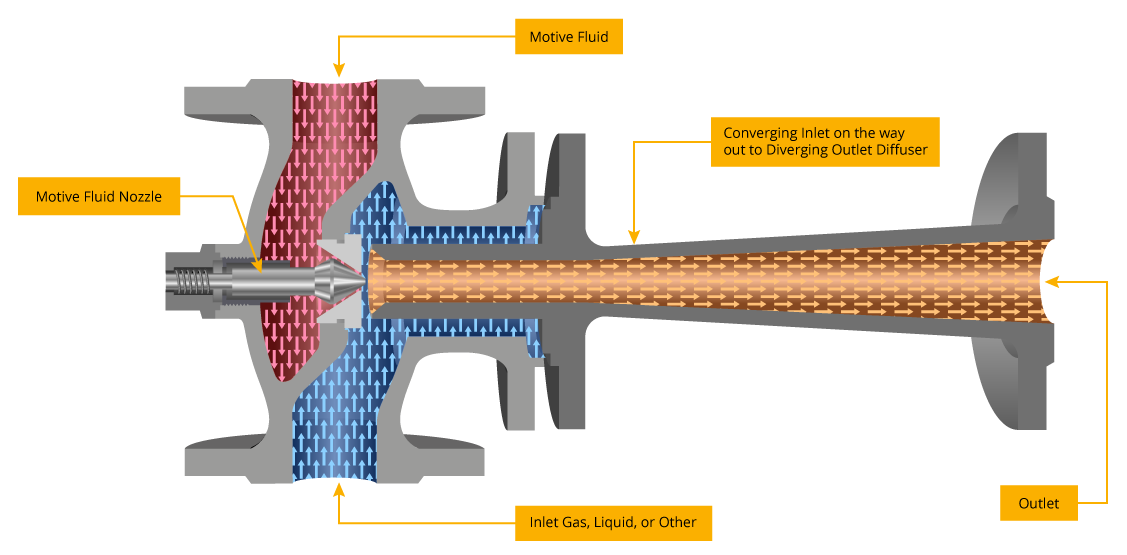
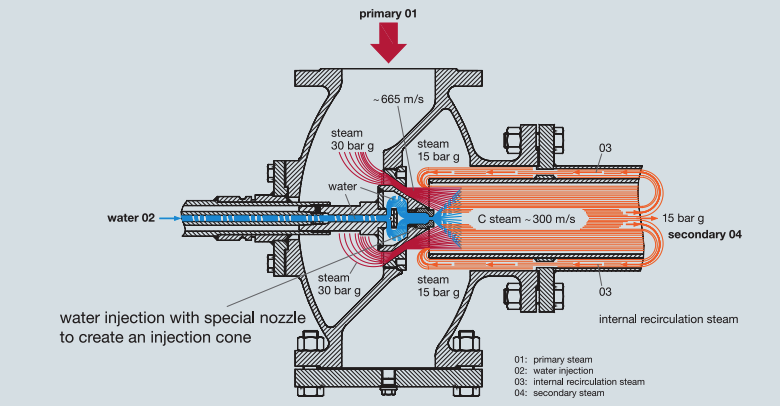
Ejector pumps (also called jet pumps) are a special version of a 3-way valve that works based on a fluid dynamics concept known as Bernoulli’s principle: pressure and fluid velocity are inversely proportional causing the Venturi effect. Ejector pumps are controlled by an electric or pneumatic actuator. These static devices mount to a pipeline system and are connected to both a high-pressure water or steam supply and another vessel with a low-pressure fluid. The ejector has two inlets leading to a nozzle, which is incorporated into an asymmetrical, hourglass-shaped tube called a diffuser. The components are often made of brass, cast iron, carbon steel, or stainless steel for durability and low maintenance, effectively offering longer lifespan and energy-saving service.
High-pressure steam or water, called the motive fluid, enters through one inlet and passes through the nozzle, which converts its pressure to velocity. As speed increases, a vacuum forms and the lower-pressure fluid is drawn in through the suction inlet.
Industries are increasingly converting their mechanical pumps to water- or steam-driven alternatives. That's because steam and water ejectors are much easier to install and are powered fully by their own motive gas or fluid. This key benefit makes water and steam ejectors much more efficient than mechanical pumps, reducing costs and improving system reliability for diverse industrial applications.
Linear actuators provide a push or pull motion along a single drive axis. They are key components in many machines, where they enable smooth and precise lifting, sliding, tilting, or dropping. Electric linear actuators, in particular, convert electrical energy into linear motion with high accuracy and speed, features that make them a popular choice for applications requiring controlled and precise movement.
Choosing the correctly sized control valve makes all the difference in controlling flow rates and managing fluid operations. Valves that are either too big or too small can jeopardize fine-tuned operations and make it impossible to ensure a consistent, standardized flow rate. Here, we provide a list of what is needed to properly size control valves, including why this step is very important with insuring long life and little to no maintenance.
Desuperheating is an important process that is used in a variety of industrial settings, including power plants, chemical plants, and natural gas processing facilities. In simple terms, desuperheating is the process of reducing the temperature of superheated steam or gases to a desired level before they are used in downstream processes. This process is necessary to ensure that the steam or gases are at the proper temperature to prevent damage to equipment and to improve the efficiency of the overall process.
Ejectors are small units within a heated fluid system that can distribute that fluid evenly throughout a defined area. Ejectors work without pumps; they use the Venturi principle to release and distribute either steam or heated water (depending on the system). At Baelz North America, we supply controllable pneumatic and electric ejectors, which each have a suction inlet, motive inlet, and discharge outlet arranged as a three-way valve to discharge the fluid. Learn more about the differences between our steam and water ejectors for various systems.
Steam and water ejectors are used in a range of industries as an alternative to mechanical pumps. They're easy to install and operate, and because they require no power aside from the motive gas or fluid, they're efficient and cost-effective. When deciding whether a steam or water ejector is right for your application, it's first important to understand how they work.
At Baelz North America, we are a premier distributor of control components and systems. One of our main offerings is control valves, which play a vital role in a wide range of industries and applications. The following guide provides an overview of these critical components, highlighting what they are, benefits of using them, typical applications, and assembly solutions available at Baelz NA.
What Is Process Heating and Cooling?
Many industries rely on process heating and cooling, both of which serve different purposes.